Gallbladder
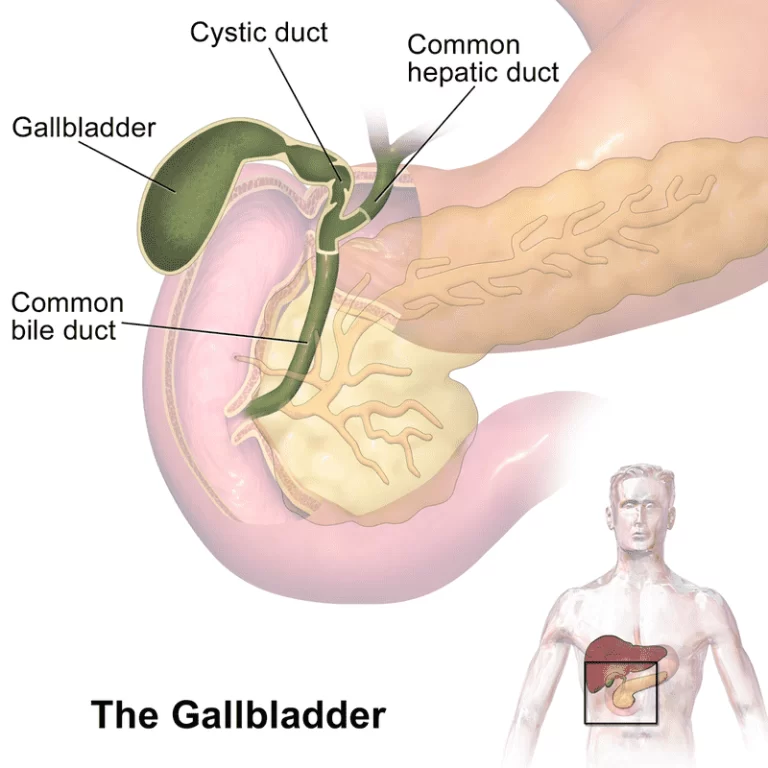
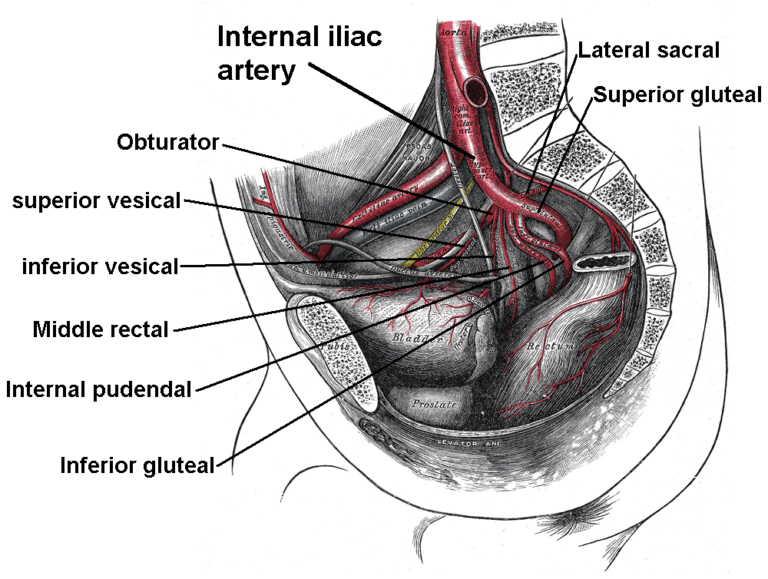
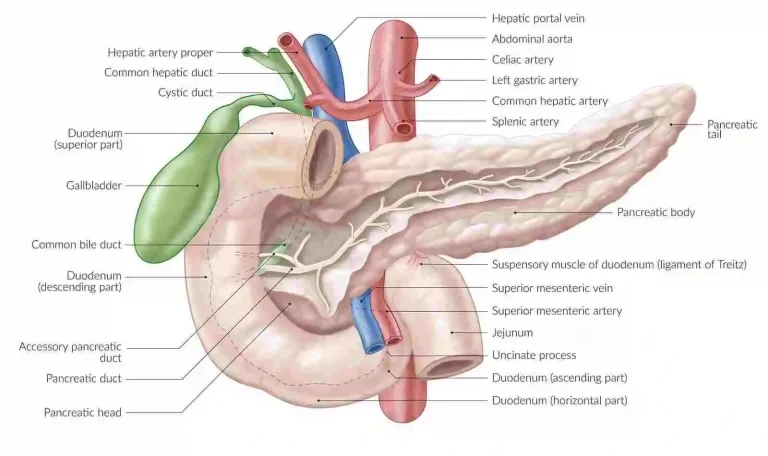
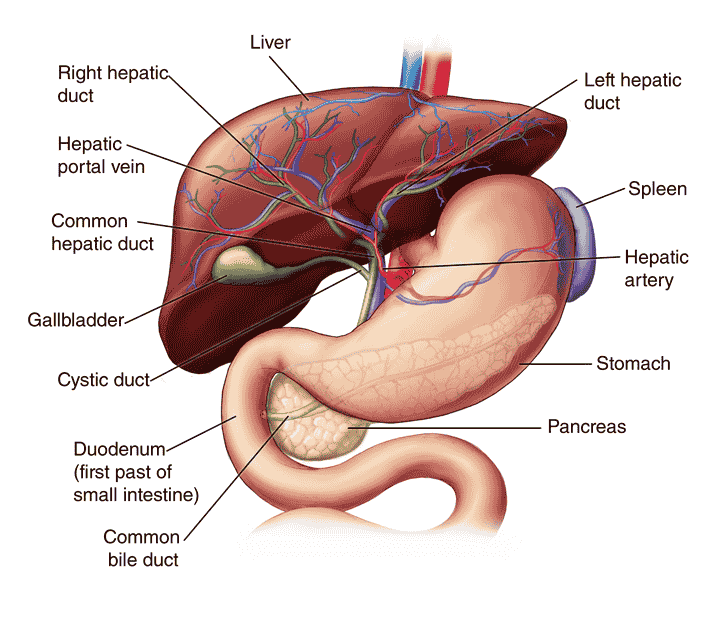
Introduction Gallbladder, an emulsion that gets created from the liver and is important for bowel movements, is accumulated and concentrated in the gallbladder, a muscular transparent sac. The material that your liver establishes to aid in the metabolism of fats in food is identified as bile. It resides directly around your liver. Gallstones, which are…